Will Traditional Banking Transition to Blockchain Models? Exploring the Future of Finance
In a world where technology is rapidly reshaping industries, many wonder: will traditional banking transition to blockchain models? This article examines the trajectory towards blockchain within banking, highlighting key movements, industry examples, and potential hurdles in the landscape of financial services. Navigate through the realities of current blockchain adoption and the compelling reasons that banks may, or may not, continue to integrate this technology.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain technology offers a solution to the inefficiencies and challenges of traditional banking, such as slow transactions and high fees, by enhancing security, transparency, and process efficiency.
- Central Banks are exploring the use of blockchain through Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) which could significantly influence monetary policy and financial inclusion, while also posing challenges for financial stability.
- Real-world applications of blockchain in banking are demonstrating tangible benefits, as financial institutions like HSBC and J.P. Morgan integrate blockchain to streamline operations and enhance trade finance, despite facing regulatory and technological challenges.
The Shift in Traditional Banking
Significant changes have marked the banking industry in recent years. Since 2008, the traditional banking landscape has witnessed a transformation, with a decrease in return on equity from 15.2% to 9% and tier-1 capital ratios varying between 9% to 13%. This paradigm shift has been driven by a variety of factors, including the need for enhanced security, competition with FinTech, and the necessity to overcome process inefficiencies within the rapidly developing digital landscape.
Historically, banks have provided a range of services from savings accounts to loans. Now, they are looking to enhance these services through digital reforms, which have the potential to lessen banking costs by 60-80%. Banks have been prompted to spearhead partnerships and digital innovations within the banking ecosystem, enhancing customer experiences and infusing their systems with resilience and efficiency through regulatory collaborations.
The limitations of traditional banking
Despite making considerable progress in adapting to the digital age, traditional banks continue to grapple with numerous constraints. Some of the most prominent issues are:
- Slow pace of transactions
- High fees associated with transactions
- Delays in cross-border payments, with the average bank transfer taking several days to complete
- High transaction costs, adding further friction to the process
These challenges highlight the need for innovation and improvement in the traditional banking system, particularly in traditional banking processes.
Additionally, the rigidity of traditional core banking systems impedes innovation due to the risk of system-wide disruptions. Banks are also subject to stringent regulatory standards, leading to substantial compliance costs that can be particularly challenging for smaller institutions. The costs associated with running physical bank branches further impact the overall profitability of traditional banking, making it less competitive compared to digital alternatives.
Blockchain as a solution
In response to these challenges, blockchain technology emerges as a compelling solution. It serves as a decentralized ledger that facilitates transparent and speedy transactions, addressing core inefficiencies of traditional banks. By enhancing trust, transparency, and introducing innovative solutions to manage bad debts, ensure regulatory compliance, and mitigate risks, blockchain can modernize operations within the banking sector.
Furthermore, blockchain’s immutable nature allows for a tamper-proof record of transactions, streamlining regulatory reporting and compliance, reducing manual workload, and guaranteeing data integrity. It also provides a secure mode for personal lending and maintains a decentralized registry of payment history, improving the lending system. Alongside these benefits, the global market for blockchain technology in banking is anticipated to grow significantly from $7.4 billion in 2022 to $94.0 billion by 2027.
Blockchain’s Influence on Central Banks

The potential of blockchain technology has not gone unnoticed by central banks. They are exploring its use with growing interest in the adoption of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). CBDCs, seen by central banks as safer alternatives to cryptocurrencies, could bolster the overall security of the digital asset landscape.
Moreover, the adoption of blockchain technology could significantly affect the transmission of monetary policy by central banks, potentially altering how economic policy shocks impact the financial system. This indicates that blockchain could usher in changes not only at the level of individual banks but also at the level of the global financial system itself.
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)
But what exactly are CBDCs? CBDCs are digital representations of a country’s physical currency, backed by the government and considered legal tender. They are not to be confused with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Instead, they are state-issued and regulated, offering a level of security and stability that cryptocurrencies often lack.
The roll-out of CBDCs could either tighten or loosen financial conditions, acting as a shock to the system with significant implications for financial markets and financial inclusion. For instance, the Swedish Central Bank’s e-krona project exemplifies a real-world CBDC implementation, utilizing R3 Corda distributed ledger technology.
Benefits and challenges of CBDCs
The potential benefits of CBDCs are clear. They can extend financial services to unbanked populations by facilitating transactions through accessible mobile devices, circumventing the need for traditional bank accounts. This could foster greater financial inclusion, especially in developing countries where access to traditional banking services is often limited.
However, the advent of CBDCs also brings its unique set of challenges. The impact of CBDCs on monetary policy is expected to be moderate under normal economic conditions but could become significant in scenarios with low-interest rates or financial market stress. Therefore, careful consideration and planning are necessary to ensure CBDCs serve their intended purpose without disrupting the financial stability.
Integrating Blockchain into Financial Institutions
Financial institutions, recognizing the potential advantages of blockchain technology, are progressively exploring its integration into their operations. This integration can enhance security and efficiency across various banking processes, from transaction validation to risk management. The adoption of blockchain in finance is driven by its features, including immutability, accuracy, consensus, trust, and transparency.
Blockchain use cases in banking range from streamlining traditional processes to revolutionizing operations in areas such as lending, trading, and payment processing. However, the shift to modern systems involving blockchain technology requires banks to embrace new technologies in all aspects of their operations.
Streamlining operations
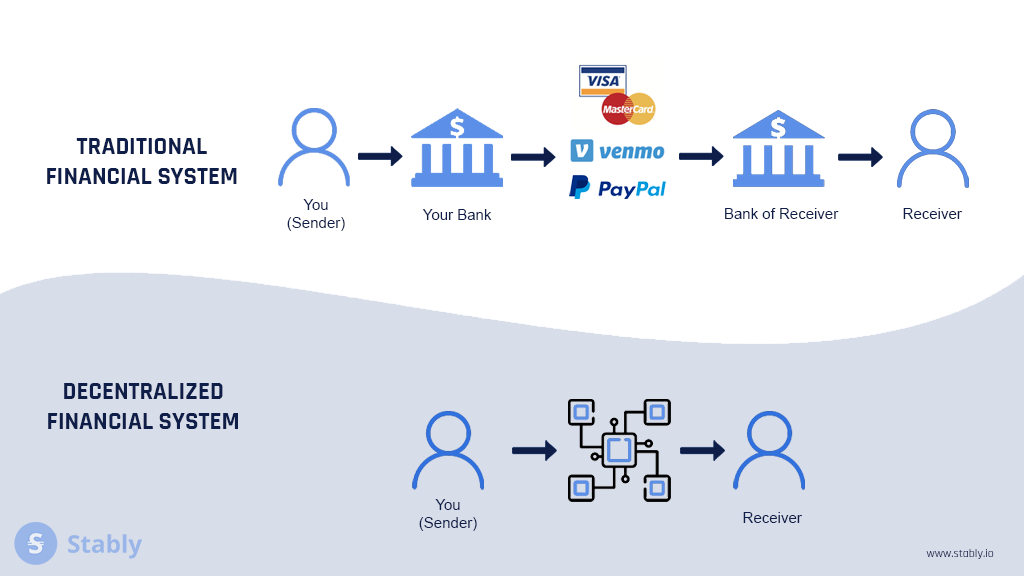
Streamlining processes stands as one of the primary benefits of integrating blockchain into banking operations. Mobile wallets using blockchain technology enhance the security and efficiency of payment services, aiming to reduce costs and improve overall payment system performance.
Moreover, blockchain can:
- Expedite transactions
- Significantly decrease cross-border payment times and costs
- Leverage cryptocurrencies’ and other blockchain solutions’ ability to bypass traditional financial intermediaries
- Enable more streamlined personal loan approvals through its decentralized registry of payment history
- Streamline trade finance processes by securing the exchange of trade documents, as demonstrated by HSBC’s Digital Vault platform.
Enhancing security and transparency

In addition to streamlining operations, blockchain technology offers the following benefits in banking:
- Boosts security by recording transactions on an immutable ledger
- Increases transparency by providing a clear and auditable record of transactions
- Reduces risks associated with inaccuracies and fraud
The transparent nature of blockchain provides a secure and shared database, enhancing real-time tracking and verification processes for financial institutions. Blockchain-based systems strengthen security within banks by:
- Decentralizing the storage of information
- Managing digital identities
- Reducing single points of failure
- Minimizing identity theft occurrences.
Moreover, smart contracts on the blockchain can automatically enforce contract terms, leading to faster processing and reduced operational costs for banks.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain Adoption in Banking
The potential of blockchain technology extends beyond theory. Major financial institutions around the globe are already harnessing its power to enhance their operations and deliver superior service to their customers. These real-world implementations can provide valuable insights into the practical benefits and challenges of blockchain adoption in banking.
HSBC, for example, has embraced blockchain technology through various initiatives, such as membership in the eTradeConnect and participation in the Contour platform to enhance trade finance operations. HSBC’s involvement in these platforms has facilitated over 18 trade transactions valued at more than USD 35 million, demonstrating the real-world applications of blockchain in streamlining trade finance.
J.P. Morgan
J.P. Morgan, a leading global financial services firm, is another prime example of a traditional bank leveraging blockchain technology. The bank developed Quorum, a blockchain platform focused on financial applications such as interbank payments.
Through the use of Quorum, J.P. Morgan introduced a programmable payments feature in its JPM Coin System, representing a permissioned ledger technology designed for efficient dollar transfer among clients. This has allowed J.P. Morgan to enhance the processing time of large payments, indicating a significant advancement in trading and compliance measures.
HSBC
HSBC, one of the world’s largest banking and financial services organizations, has also made significant strides in blockchain adoption. The bank has introduced a trade finance platform based on blockchain technology. It is aimed at digitalizing and simplifying operations..
The platform utilizes the R3 blockchain, allowing HSBC to tap into blockchain’s benefits for financial transactions. By enabling the secure sharing of trade documents among participants, HSBC’s Digital Vault demonstrates how blockchain can enhance transparency and efficiency in trade finance operations.
Overcoming Challenges in Blockchain Adoption
Despite the clear benefits of blockchain technology in banking, its adoption does not come without challenges. Banks face multiple hurdles when integrating blockchain into their operations, including:
- A variety of risks, such as cybersecurity threats and potential fraud
- Technological complexities, such as scalability and interoperability issues
- Organizational restructuring to accommodate the new technology
- Adherence to regulatory compliance and legal frameworks
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of organizational restructuring, technological advancements, and adherence to regulatory compliance.
In order to surmount regulatory challenges, banks could consider:
- Forging partnerships with reliable software development companies
- Laying down clear guidelines for blockchain adoption
- Ensuring the presence of robust governance frameworks
This can help banks navigate the regulatory landscape and successfully implement blockchain in their operations.
Regulatory compliance
A key challenge in blockchain adoption is regulatory compliance. However, blockchain itself facilitates better regulatory reporting and compliance in banking by maintaining a tamper-proof record of transactions.
Ensuring strict adherence to international regulations is critical in blockchain implementation in the banking sector. The immutable nature of blockchain provides a reliable and secure means to meet stringent regulatory compliance requirements in the banking industry.
Technological hurdles
In addition to regulatory challenges, banks also face technological hurdles when adopting blockchain. One of these is the scalability issue, which makes it challenging for blockchain to handle the high volume of transactions typically processed by banks.
Moreover, the banking industry must address the following issues to ensure seamless communication between various blockchain networks and traditional banking systems:
- Interoperability issues
- Technological barriers
- Efficient scalability solutions
- Industry-wide standardization
- Robust practices for blockchain integration
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for the successful integration of blockchain technology in the banking sector.
The Future of Banking: A Hybrid Model
Envisioning the future of banking, it may involve a hybrid model that amalgamates the reliability of traditional banking with the efficiency of decentralized finance (DeFi). Hybrid blockchain solutions, combining private and public blockchain networks, offer a promising framework for the evolution of the banking industry.
These hybrid models leverage the advantages of private blockchains, such as smart contracts, high performance, and thorough auditability, alongside the enhanced transparency and verifiability of public blockchains. Hybrid blockchains also make it possible to meet regulatory compliance by keeping sensitive data off the public ledger, addressing privacy concerns in the financial sector.
Decentralized finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance, also known as DeFi, is a blockchain offshoot focusing on innovative solutions in the financial sector. It leverages blockchain to create more accessible, efficient, and transparent financial services. Cryptocurrency, a digital or virtual currency using cryptography for security and operating on decentralized blockchain networks, lays the groundwork for the development of DeFi.
DeFi platforms are capable of facilitating banking functions such as loan agreements, insurance claims processing, and the creation of derivative contracts. By providing financial services on a decentralized platform, DeFi holds the potential to empower economically and integrate unbanked populations globally.
Asset tokenization
Another promising application of blockchain technology in finance is asset tokenization. It allows fractional ownership of real assets and easier transferability, enhancing liquidity in financial markets.
The Onyx Digital Assets network, launched by J.P. Morgan in 2020, enables the tokenization of traditional assets like U.S. Treasuries and money-market products, while BlackRock has utilized the Tokenized Collateral Network for tokenizing shares in money market funds. Blockchain technology, therefore, facilitates fractional ownership and easier transferability of assets such as real estate, stocks, and bonds.
Summary
Blockchain technology, once seen as a disruption to the financial industry, is now being embraced as a catalyst for innovation and advancement. With its ability to streamline operations, enhance security, and provide unparalleled transparency, blockchain technology holds the potential to transform the banking industry. While challenges remain, the benefits of blockchain integration in banking far outweigh the hurdles. As banks continue to explore and adopt blockchain, a new era of efficient, secure and inclusive banking is on the horizon.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between blockchain based banking and traditional banking?
The main difference between blockchain-based banking and traditional banking lies in the automation and enhanced security provided by blockchain. Blockchain lowers transaction costs through automation and reduces fraud and cyber threat risks through encryption and decentralization.
How blockchain will revolutionize banking?
Blockchain will revolutionize banking by automating and enforcing contract terms without intermediaries, reducing processing times and costs, and allowing for various applications such as loan agreements and insurance claims processing through DeFi platforms.
Will banks be replaced by crypto?
Decentralized blockchain-based solutions offer faster transactions, increased security, and lower fees, but it is unlikely that they will fully replace banks in the near future due to various challenges and complexities.
How does blockchain technology improve traditional banking?
Blockchain technology improves traditional banking by streamlining operations, enhancing security, and providing transparency. It allows for faster and more efficient transactions, reduces the risk of fraud, and enables better regulatory compliance.
What are Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)?
CBDCs are digital representations of a country’s physical currency, backed by the government and deemed as legal tender. They differ from cryptocurrencies as they are state-issued, regulated, and offer a level of security and stability that cryptocurrencies often lack.

