Bitcoin Price Analysis: Top Factors Influencing Today’s Market
Bitcoin is a groundbreaking digital currency, and its price is a topic of great interest. This article will explain what influences Bitcoin’s price today and what you need to know.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin’s transformation from a niche digital currency to a leading financial asset highlights its resilience and potential for growth amid regulatory fluctuations and market dynamics.
- Bitcoin’s blockchain technology ensures transaction security and transparency while its mining process engages a competitive environment to validate transactions and generate new coins.
- Legal recognition and regulatory clarity significantly impact Bitcoin’s market valuation and investor participation, making the regulatory landscape crucial for its adoption and growth.
Bitcoin’s Historical Background

Bitcoin’s story began on October 31, 2008, when an individual or group of individuals using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. This whitepaper laid the foundation for a decentralized digital currency that operates without a central authority.
On January 3, 2009, Nakamoto mined the first block of Bitcoin, known as the genesis block. Hidden within this block was a message referencing a newspaper headline about bank bailouts, hinting at the motivations behind Bitcoin’s creation. In the early days, Nakamoto mined approximately 1 million bitcoins before disappearing from public involvement, leaving a legacy shrouded in mystery.
Introduced in 2009, Bitcoin quickly became the leading decentralized crypto by market capitalization over the past decade and is expected to continue its influence in the next decade. Its transformation from a niche experiment to a global financial asset has been remarkable.
Key Milestones in Bitcoin’s Journey

Bitcoin’s early days saw it primarily used as a currency among enthusiasts. However, it wasn’t until 2011 that Bitcoin’s price surpassed $1, marking its first major milestone. This was just the beginning of Bitcoin’s remarkable ascent.
In 2013, Bitcoin gained mainstream attention when Forbes recognized it as a top investment option. By the end of 2020, Bitcoin’s value had surged to nearly $29,000, driven by increasing institutional interest and broader acceptance. The following year, Bitcoin reached an all-time high of $69,000, fueled by significant institutional investments.
Despite its meteoric rise, Bitcoin’s journey has not been without challenges. Key events include:
- In the summer of 2021, Bitcoin experienced a sharp 50% price drop, highlighting its inherent volatility.
- Bitcoin’s resilience was evident as it began 2023 at $16,530.
- Bitcoin later peaked at over $100,000 in 2024 following the approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs by the US SEC.
These milestones underscore Bitcoin’s dynamic nature and its ability to recover and thrive despite market fluctuations and regulatory hurdles.
Understanding Bitcoin Blockchain Technology
At the heart of Bitcoin is its blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger that ensures transparency and security. Each block in the Bitcoin blockchain contains transaction data linked in chronological order through cryptographic hashes. This structure makes it nearly impossible to alter a block without affecting all subsequent blocks, ensuring the immutability of the data.
Transactions on the Bitcoin network are confirmed roughly every ten minutes, requiring multiple nodes to reach consensus for validation. This mechanism ensures data integrity and prevents fraud.
Blockchain technology provides transparency, as all transactions are publicly viewable while maintaining user anonymity through wallet addresses. This unique combination of transparency and privacy has contributed to Bitcoin’s widespread adoption and trust among users.
Bitcoin Mining Explained
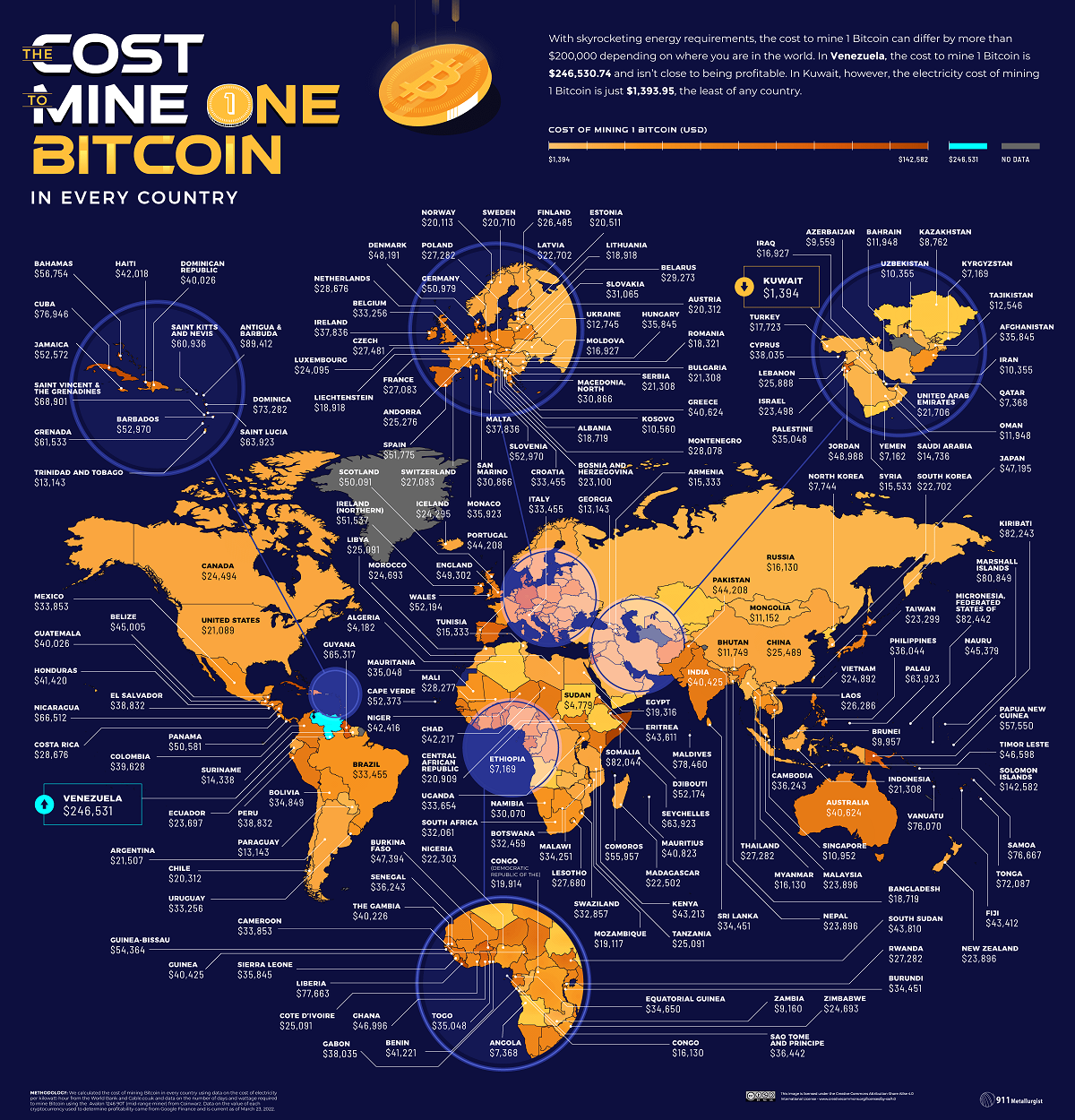
Bitcoin mining is the process of validating and recording transactions on the Bitcoin network while generating new bitcoins. The process involves:
- Miners competing to solve complex cryptographic puzzles.
- The first miner to solve the puzzle adds a new block to the blockchain and earns a reward.
- The process is secured by the SHA-256 hashing algorithm, which produces a unique hash for each block.
Mining requires specialized hardware, such as ASICs, optimized for processing the complex calculations involved in mining. The difficulty of generating a block is adjusted every 2,016 blocks to maintain an average of ten minutes between new blocks.
Electricity consumption is a significant factor affecting the profitability of Bitcoin mining, as it requires substantial energy to run mining operations. Key aspects of Bitcoin mining include:
- Miners often join mining pools to increase their chances of earning Bitcoin rewards by sharing computational resources and risks.
- Mining involves grouping transactions into blocks.
- A Merkle tree is used to summarize and verify the transactions within each block.
Bitcoin Wallets: Types and Security
Bitcoin wallets securely store and manage bitcoins, with types ranging from hardware wallets to cold storage options. Hardware wallets offer a balance of security and user-friendliness, ensuring Bitcoin’s safe storage.
Key practices for securing Bitcoin wallets include:
- Using cold storage wallets to keep private keys offline, reducing theft risks from online attacks.
- Keeping only small amounts of Bitcoin in online wallets to minimize risk.
- Making regular backups to ensure fund recovery in case of loss or theft.
Encrypting your wallet adds security by requiring a password for funds access. Multi-signature wallets enhance security with multiple transaction approvals. These practices help secure Bitcoin assets and mitigate digital currency risks.
Bitcoin’s Role as Digital Gold

Bitcoin is often referred to as “digital gold” due to its characteristics that mirror those of physical gold. It serves as a non-sovereign store of value, though it has not yet matched gold’s long-standing societal acceptance. Its limited supply and inflation resistance bolster Bitcoin’s reputation as digital gold.
Bitcoin as digital gold underscores its potential as a reliable store of value during economic downturns. Emerging markets, especially those with unstable currencies, may increasingly adopt money.
Unlike traditional gold, Bitcoin’s digital transferability and storage enhance its appeal as a modern asset. With a capped supply of 21 million coins, scarcity directly impacts its price. Its status as the first and most well-known cryptocurrency helps maintain market dominance despite slower transaction speeds.
Scalability Challenges and Solutions
Bitcoin’s blockchain can handle approximately 7 to 10 transactions per second, significantly lower than traditional payment systems like Visa. This limitation poses a significant challenge for Bitcoin’s scalability. The scalability trilemma suggests that a network can optimize only two out of three traits: decentralization, security, and scalability, often requiring trade-offs.
Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network can facilitate faster and cheaper Bitcoin transactions by allowing off-chain processing. Advancements in blockchain technology, like the Lightning Network, are expected to improve transaction speed and reduce costs for Bitcoin users.
The Lightning Network serves as a potential scaling solution by enabling high transaction throughput without compromising the main blockchain. These solutions are crucial for Bitcoin to maintain its growth and adoption in the face of scalability challenges.
Legal Status and Regulatory Environment
Legal recognition of Bitcoin significantly influences its adoption. Countries with clear international regulations often experience robust market activity and investment, while unclear regulations in other regions hinder growth and adoption.
Uncertain legal frameworks can deter institutional investors, affecting Bitcoin’s market valuation. The regulatory landscape varies, with some nations banning it while others promote its use. Evolving regulations may enhance investor trust and participation, encouraging them to invest and investing in the market.
Bitcoin’s success is closely tied to its legal status in the world, making the regulatory environment crucial for all investors.
Bitcoin as an Investment

Bitcoin’s capped supply of 21 million coins underpins its value, distinguishing it from fiat currencies. Halving events reduce supply and can trigger significant price increases due to heightened demand.
Bitcoin’s volatility has decreased over time, now less volatile than many well-known stocks like Netflix. Historically, low volatility precedes significant price increases. As of early 2024, Bitcoin’s one-year realized volatility fell below 50%, a rare occurrence.
From 2020 to early 2024, Bitcoin’s Sharpe ratio of 0.96 indicates favorable risk-adjusted returns. A Sortino ratio of 1.86 suggests most volatility has been positive. Institutional adoption is growing, with major firms integrating Bitcoin into their portfolios, recognizing it as a legitimate store of value.
Investor sentiment during low volatility often reflects selling pressure exhaustion. Bitcoin’s price surged 150% in 2023 amid declining realized volatility, showcasing its investment potential to sell.
Market Dynamics and Price Influencers
Market dynamics are influenced by factors like ownership concentration and regulatory changes. About 27% of bitcoin is held by the top 0.01% of holders, showing heavy ownership concentration. A 2024 Pew Research Center survey found 17% of American adults engaged with cryptocurrency, indicating growing demand. The percentage of bitcoin held by the top holders highlights the significant distribution in the market.
Regulatory changes significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. For example, China’s complete trading ban in February 2018 caused a price crash. Trading volume fluctuations among exchanges also affect price stability and trends.
Regulatory changes and market events contribute to Bitcoin’s price volatility. In early 2025, the average transaction fee was about $1.63, reflecting significant changes in transaction costs affecting market activity.
Bitcoin Transactions and Fees
Bitcoin transaction fees vary depending on network activity:
- Fees are higher during busy periods due to increased competition for block space.
- Fees are calculated based on transaction size in bytes.
- Larger transactions incur higher fees due to increased data load.
Users can lower Bitcoin transaction fees by opting for slower confirmation times during off-peak hours. High increased fees can deter spending, causing some to seek alternative cryptocurrencies to pay for lower-cost transactions and to consider an exchange for better options.
Understanding how transaction fees work and implementing strategies to minimize costs can help users make more efficient use of Bitcoin for transactions.
Privacy and Anonymity in Bitcoin
Bitcoin transaction privacy is compromised by the public nature of the blockchain, where transaction details are visible to all. Although Bitcoin offers some privacy, it’s often not effectively utilized, leading to misconceptions about its traceability.
Understanding adversaries’ methods to analyze transaction data can help consumers protect their identities and privacy. Non u blockchain attacks, like traffic analysis, can expose users by monitoring network communications and revealing patterns in their account activities.
Users can enhance anonymity by using new addresses for each transaction and techniques like CoinJoin to obscure ownership. Financial privacy is crucial for Bitcoin’s fungibility; traceable coins undermine their value.
Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin Cash, created in 2017 from a hard fork, has an 8MB block size compared to Bitcoin’s 1MB, enabling faster transactions. Litecoin’s maximum supply is 84 million coins, four times greater than Bitcoin’s, with faster transaction times.
EOS aims to enhance scalability, claiming millions of transactions per second, while Bitcoin processes about seven. Ripple supports a bank-used payment network and can exist without its cryptocurrency, XRP.
Stellar facilitates multi-currency transactions, with Lumens playing a role in fees to prevent spam. Ethereum’s Ether serves as currency and powers decentralized applications and smart contracts on its network.
Cryptocurrencies’ varying supplies influence their market values. Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash are capped at 21 million coins, while others like Ether have no fixed limit.
Future Prospects for Bitcoin
Experts predict Bitcoin could reach $126,180.47 by September 2025, highlighting potential significant price fluctuations in the preceding months due to market dynamics and global economic factors.
Bitcoin’s price is expected to remain volatile short-term due to global economic factors. A bullish trend could emerge with continued institutional adoption. Increasing interest from major corporations and financial institutions may boost price stability and enhance Bitcoin’s investment credibility. We expect that these developments will further influence the market and forecasts.
Competitive pressures from altcoins and stablecoins may divert investments from Bitcoin, challenging its dominance. Nonetheless, Bitcoin’s established reputation and growing institutional interest suggest it will continue to play a significant role in the cryptocurrency market.
Summary
Bitcoin’s journey from a niche digital experiment to a global financial asset has been marked by significant milestones, technological advancements, and market dynamics. Understanding its historical background, the underlying blockchain technology, and the factors influencing its market price is crucial for anyone looking to engage with Bitcoin.
As we look to the future, Bitcoin’s potential remains vast, driven by its unique characteristics as digital gold and its growing acceptance among institutional investors. Whether you are an investor, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the world of cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin offers a fascinating glimpse into the future of finance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the genesis block in Bitcoin’s history?
The genesis block is significant as it represents the official start of Bitcoin’s blockchain, encapsulating the ideological motivations for its creation through a hidden message about bank bailouts. This event is foundational for understanding Bitcoin’s purpose and inception in response to financial crises.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Bitcoin mining works by validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain, with miners competing to solve challenging cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle earns a reward in newly generated bitcoins.
What are the main types of Bitcoin wallets, and how do they differ in terms of security?
The main types of Bitcoin wallets are hardware wallets and cold storage wallets, with hardware wallets offering robust security and user-friendliness, and cold storage wallets significantly minimizing theft risk by keeping private keys offline. Ultimately, choosing the right wallet depends on your security needs and comfort level with technology.
Why is Bitcoin often referred to as “digital gold”?
Bitcoin is referred to as “digital gold” due to its limited supply and characteristics that make it a reliable store of value, akin to physical gold, particularly in times of economic uncertainty. This analogy highlights its role as a non-sovereign asset with inflation-resistant qualities.
What are the future prospects for Bitcoin?
The future prospects for Bitcoin appear promising, with predictions suggesting it could reach a maximum price of $126,180.47 by September 2025. While short-term volatility may persist, increased institutional adoption could drive a bullish trend despite competitive pressures.

