Whats Happening with Bitcoin Mining After the 2024 Halving: Insights & Predictions
After the 2024 halving, Bitcoin mining becomes less profitable as block rewards drop from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC. This change pushes miners to innovate and rethink their strategies. This article delves into what’s happening with Bitcoin mining after the 2024 halving, covering immediate impacts, technological shifts, and economic implications.
Key Takeaways
- The 2024 Bitcoin halving has reduced miners’ rewards from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, prompting many to re-evaluate their strategies to maintain profitability.
- Post-halving, transaction fees and Bitcoin’s price will play crucial roles in sustaining mining profitability as block rewards decrease, particularly for larger operations.
- Innovations in mining technology, energy management, and geographical shifts towards renewable energy sources are essential adaptations for miners facing a more competitive landscape.
Immediate Effects of the 2024 Bitcoin Halving on Mining

The 2024 Bitcoin halving event has slashed the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, halving the income that miners receive for each new block they mine. This immediate reduction in rewards forces miners to re-evaluate their operational strategies. For many, especially those with higher operational costs, the reduced rewards can make mining less viable, prompting them to either upgrade their technology or exit the market altogether. This creates a more competitive landscape, rewarding those who can innovate and operate efficiently.
The halving also leads to a consolidation within the mining community:
- Smaller, less efficient miners might find it challenging to remain profitable and could be forced to shut down their halved operations.
- This consolidation can reduce the number of active miners on the Bitcoin network. Halving reduces the number of miners, making those who remain likely to be more efficient and better equipped to handle the lower rewards. Additionally, understanding how halving affects bitcoin is crucial for all participants in the market. After the halving occurred, these dynamics become even more significant. Furthermore, the rewards for miners will halve, impacting their operations.
Effective planning and risk management become crucial as miners navigate these changes to continue contributing to the Bitcoin blockchain while maintaining profitability through blockchain technology.
Mining Profitability Post-2024 Halving

The halving event has cut miners’ income from block rewards in half, significantly impacting mining profitability. However, several factors can help sustain profitability in the post-halving landscape:
- The price of Bitcoin itself. As of early April 2024, Bitcoin’s price ranged between $65,000 and $70,000, supporting miner profitability even with reduced rewards.
- If Bitcoin’s price increases, it can turn a revenue loss measured in Bitcoin into a profit when measured in fiat currency.
- This means that the value of the revenue in traditional currency can increase.
Another crucial factor is the role of transaction fees. As block rewards diminish, transaction fees become a more significant revenue stream for miners. Factors that help maintain mining profitability include:
- Increased demand for transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain, which can drive up transaction fees and help compensate miners for lower block rewards.
- Decreasing electricity costs.
- Technological advancements in mining hardware.
However, the landscape is not without its challenges. Smaller individual miners face lower chances of profitability due to decreased rewards, making it difficult for them to compete with larger, more efficient operations. This dynamic can lead to a more centralized mining industry, where only the most efficient and technologically advanced miners thrive.
Despite these challenges, the overall profitability of bitcoin mining remains viable as long as the price stays above certain thresholds, ensuring that maintain profitability continues to be an attractive venture.
Adaptations by Bitcoin Miners
In response to the reduced mining rewards post-halving, Bitcoin miners are adapting in several innovative ways. These adaptations are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and profitability in a more competitive environment. From leveraging cutting-edge technologies to optimizing energy costs and exploring new geographical locations, miners are deploying a variety of strategies to stay ahead.
Let’s delve into these adaptations in more detail.
Technological Innovations in Mining Hardware
One of the most significant adaptations by bitcoin miners is the adoption of advanced specialized hardware. Recent advancements in ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) design have led to greater energy efficiency and higher hash rates, significantly benefiting mining profitability. These new ASIC models are not only more powerful in terms of computational power but also more cost-effective, allowing miners to process more transactions while consuming less energy.
The technological evolution in ASIC hardware has revolutionized the mining industry. New generations of ASIC miners are significantly more power-efficient compared to earlier models, making it possible to achieve higher profitability even as block rewards decrease. This increased efficiency helps miners stay competitive and continue contributing to the Bitcoin network, despite the halving event’s impact on rewards.
Energy Cost Management
Managing energy costs is another critical adaptation strategy for bitcoin miners. By adopting strategic energy agreements, miners can secure lower electricity rates, enhancing their overall operational margins. Investments in energy efficiency technologies, such as advanced cooling systems and energy storage solutions, further help in reducing operational expenses.
Sustainability concerns are also driving miners to focus on green mining practices. Sourcing energy from renewable resources and managing emissions allows miners to comply with environmental standards and reduce their carbon footprint.
These efforts not only improve operational efficiency but also align with the growing emphasis on sustainability within the cryptocurrency industry.
Geographical Shifts for Cheaper Energy
In pursuit of lower energy costs, many bitcoin miners are relocating to regions with abundant renewable energy resources. Countries with favorable mining regulations, such as Kazakhstan, attract miners due to their lower operational costs and abundant energy supplies. This geographical shift allows miners to capitalize on cheaper energy, thereby enhancing their profitability.
Regulatory developments in these regions provide clarity and encourage capital investment in mining operations, transforming the industry into a more structured and compliance-oriented sector. By establishing operations in areas with abundant renewable energy, miners can reduce their energy costs and contribute to a more sustainable Bitcoin network.
Transaction Fees as a Revenue Stream
As block rewards continue to decrease, transaction fees are becoming an increasingly important revenue stream for bitcoin miners. These fees help offset the lower block rewards, ensuring that mining remains profitable. When the demand for transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain rises, so do the transaction fees, providing a vital source of income for miners.
The continued growth of Bitcoin’s adoption suggests a strong fee market is possible, benefiting miners reliant on transaction fees. As more users engage in Bitcoin transactions, the associated fees can significantly contribute to miners’ revenue, offsetting the impact of reduced block rewards. This shift underscores the evolving nature of mining profitability in a post-halving world.
Network Security and Mining Activity

Bitcoin network’s efficiency and security are closely linked to mining activity. Increased mining efficiency leads to quicker transaction confirmations, enhancing the overall security of the network secure. A robust hash rate, indicative of high mining activity, ensures that the Bitcoin network remains secure against potential attacks, which is particularly evident in a proof of work blockchain that is essential for verifying transactions.
However, there are potential risks associated with the centralization of mining activities and the central authority of large mining pools. If large mining pools dominate the hash rate, it could threaten the decentralized nature of Bitcoin and compromise network security. Additionally, a decline in miner activity due to reduced profitability can lead to longer transaction confirmation times, impacting the network’s security and reliability.
The network’s difficulty adjustment mechanism mitigates these risks by ensuring the time between new blocks remains around 10 minutes, maintaining stability.
Economic Implications of Reduced Supply
The halving event’s primary economic implication is the reduced supply of new bitcoins entering the market. This tightening supply is a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s deflationary nature, which helps control inflation and increase scarcity. Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been followed by price increases as the reduced supply drives up demand.
Bitcoin’s capped supply of bitcoin reinforces its perception as ‘digital gold,’ making it attractive during periods of currency inflation. When inflation spikes, one bitcoin often serves as a hedge against declining currency value, driving up demand and Bitcoin’s price as a digital asset, as central banks’ policies can influence these economic conditions.
However, during deflationary periods, the demand for Bitcoin may decrease as cash becomes more appealing, potentially leading to price drops. These dynamics highlight the complex interplay between Bitcoin’s supply, bitcoin’s deflationary nature, and broader economic conditions.
Historical Context: Comparing Past Halvings
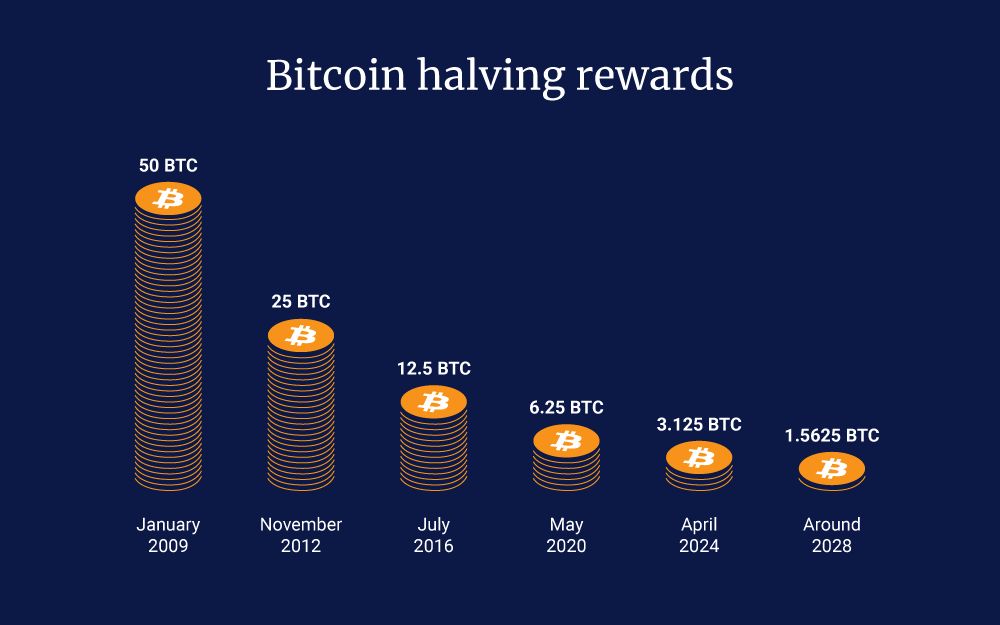
Bitcoin halvings, occurring approximately every four years, have historically had a significant impact on market dynamics. The first halving in 2012 cut the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC and was followed by substantial price growth. Similarly, the second halving in 2016 reduced the reward to 12.5 BTC, with Bitcoin’s value increasing significantly within the year.
The third halving in 2020 brought the reward down to 6.25 BTC and was associated with a dramatic price surge over the subsequent twelve months. Historical data shows that returns in the periods leading up to and following a halving are significantly higher compared to other times.
These patterns suggest that the 2024 halving could follow a similar trajectory, with potential price increases as the reduced supply and new supply impact market dynamics.
Predictions for Future Bitcoin Halvings
Future Bitcoin halvings are expected to further decrease the block reward, influencing supply dynamics and potentially increasing Bitcoin’s value if demand remains stable or grows. The interplay of reduced supply and increasing demand around halving events is likely to attract more investor attention and market activity, potentially driving up Bitcoin’s price.
The last Bitcoin halving is projected to occur around 2140, after which no new bitcoins will be issued. As we approach this final halving and the next halving, the dynamics of supply and demand will continue to play a crucial role in shaping Bitcoin’s market, influencing the rate at which new bitcoin are created. The total supply of bitcoins is capped at a maximum supply of 21 million.
Investors and miners alike will need to stay vigilant, adapting to these changes and capitalizing on the opportunities that precious metals present.
Long-Term Outlook for Bitcoin Mining
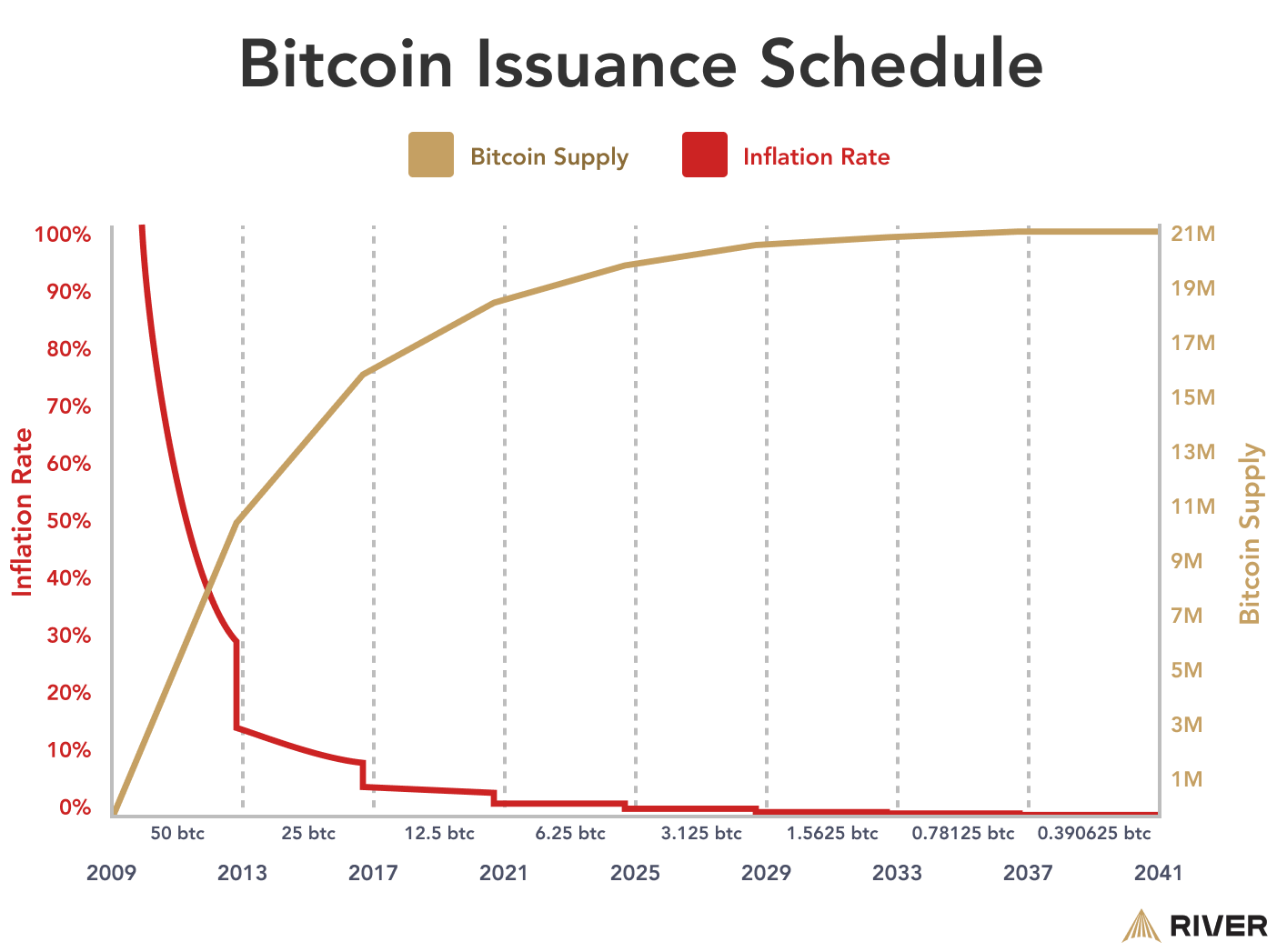
The long-term sustainability of bitcoin mining is being increasingly examined in light of market trends and technological advancements. Miners are consolidating operations to streamline costs and remain competitive in a volatile market. These consolidations could lead to fewer but larger mining operations, impacting the competitive landscape of Bitcoin mining.
As regulatory frameworks evolve, sustainability challenges will continue to shape the future of Bitcoin mining. The growing emphasis on environmental impact and energy efficiency will drive miners to adopt more sustainable practices.
Despite these challenges, the enduring value of Bitcoin and its role in the global financial system suggest that mining will remain a vital and intriguing aspect of the bitcoin ecosystem.
Key Takeaways for Investors
The anticipation surrounding halving events often leads to increased investor interest and market activity. Many expect Bitcoin prices to trend upward post-halving due to the reduced rate of new bitcoins entering circulation. The potential for value appreciation attracts more investors, making Bitcoin an intriguing asset for inclusion in an investment portfolio.
However, investors should consider several factors before diving in. The cryptocurrency mining market is projected to grow significantly, driven by technological advancements and increasing institutional adoption. Still, cryptocurrency markets reactions can be volatile, with prices sometimes dropping initially after a halving.
Investors should weigh these dynamics, market conditions, and their own risk tolerance when considering investments around halving events. In the long run, Bitcoin’s capped supply and its role as a hedge against inflation could make it a valuable addition to a diversified portfolio.
Summary
The 2024 Bitcoin halving has ushered in a new era of challenges and opportunities for miners, investors, and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem. From immediate impacts on mining profitability to long-term adaptations in technology and energy management, the halving event reshapes the landscape of Bitcoin. Historical patterns suggest potential price increases, while the evolving regulatory and technological environment will continue to influence mining practices. For investors, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed decisions. As Bitcoin continues to mature, its deflationary nature and limited supply ensure it remains a significant player in the global financial system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Bitcoin halving?
A Bitcoin halving is an event that occurs roughly every four years, cutting the block reward for miners by half, which helps to limit the supply of new bitcoins and control inflation. This mechanism is vital for maintaining the cryptocurrency’s value over time.
How does the 2024 halving affect miner profitability?
The 2024 halving will significantly impact miner profitability by reducing the block reward to 3.125 BTC, effectively halving their income. To maintain profitability, miners will need to rely on rising Bitcoin prices, increased transaction fees, and managing energy costs effectively.
What technological advancements are helping miners adapt post-halving?
Technological advancements in ASIC hardware are enhancing energy efficiency and increasing hash rates, which are crucial for improving mining profitability after the halving. As a result, miners can better adapt and maintain competitiveness in the market.
How do transaction fees impact miners post-halving?
Transaction fees become essential for miners’ profitability post-halving, as block rewards decrease. Higher transaction demand can lead to increased fees, offsetting the reduced earnings from block rewards.
What are the long-term implications of Bitcoin’s reduced supply?
The long-term implications of Bitcoin’s reduced supply include enhanced scarcity, which may lead to increased value over time. Additionally, its deflationary nature positions Bitcoin as a desirable asset, especially during inflationary periods in traditional currencies.

