Understanding Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): What They Mean for Crypto Investors
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) could reshape the financial world. Crypto investors need to know what central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) mean for crypto investors, as this entails important implications for their investments. This article will delve into how CBDCs—central bank digital currencies—could influence your crypto assets, market dynamics, and investment strategies, and what they mean for crypto investors: central bank digital currencies CBDCs what they mean for crypto investors.
Key Takeaways
- CBDCs, regulated by central banks, provide a stable and secure digital alternative to cryptocurrencies, which are decentralized and volatile.
- The implementation of CBDCs is expected to reshape the crypto investment landscape, attracting traditional investors while prompting existing crypto investors to reassess their strategies.
- As more countries adopt CBDCs, both regulatory challenges and opportunities for innovation will emerge, necessitating that investors remain informed and adaptable to navigate the evolving market dynamics.
Overview of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital forms of fiat currency issued by central banks, representing a significant evolution in the way we perceive and use money. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are digital liabilities of central banks, made widely available to the public. The primary purpose of CBDCs is to offer a safer, more stable digital asset with no associated credit or liquidity risks, ensuring privacy, transferability, convenience, accessibility, financial security, and bank digital currency cbdc.
There are two types of CBDCs. They are classified as wholesale and retail. Wholesale CBDCs are used primarily by financial institutions, while retail CBDCs are government-backed digital currencies intended for use by consumers and businesses.
Many countries view CBDCs as a supplement to their existing financial systems rather than a complete replacement, aiming to enhance the efficiency and stability of their monetary policy. This dual approach helps maintain control over growth and inflation while providing a secure means of digital payments.
Fast Fact
As of today, over 130 nations are exploring the possibility of launching their own digital currencies, with 66 countries at advanced stages of development, including pilot and launch phases. This global momentum underscores the growing recognition of CBDCs as critical tools for modernizing financial systems and offering alternatives to a country’s fiat currency and traditional banking.
Key Differences Between CBDCs and Cryptocurrencies

While both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies operate in the realm of digital currencies, their underlying principles and regulatory frameworks are markedly different. CBDCs are regulated by central authorities, designed to implement monetary policies that ensure stability, control growth, and influence inflation. In contrast, cryptocurrencies operate within a decentralized framework, challenging existing financial paradigms with their lack of central control.
The purpose of CBDCs is to enhance the efficiency of traditional banking systems, providing a stable and secure digital currency. Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, are known for their volatility and are largely driven by investor sentiments and market dynamics. This fundamental difference in purpose and regulation creates distinct pathways for these digital currencies in the financial ecosystem.
Regulation and Trust
Regulatory frameworks for CBDCs are established and enforced by central banks, ensuring a higher degree of trust and security compared to the often unregulated world of cryptocurrencies. The introduction of CBDCs could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny for the entire digital currency market, potentially impacting the operations of existing cryptocurrencies. This evolving regulatory landscape is a critical consideration for investors as CBDCs gain traction.
However, the centralized nature of CBDCs raises concerns about privacy and cybersecurity. Governments could potentially monitor transactions, leading to increased competition and innovation within the cryptocurrency market as it adapts to these new challenges. Additionally, the transition to CBDCs may disrupt existing financial systems, requiring significant adaptation from traditional banking structures.
Stability vs. Volatility
One of the most significant differences between CBDCs and cryptocurrencies is their approach to value stability. CBDCs are designed to mirror the value of fiat currencies, providing a stable digital asset aligned with traditional monetary systems. This stability is a key factor in their appeal, particularly for those wary of the dramatic price swings often associated with cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrencies are known for their volatility, with prices fluctuating based on market sentiment, usage, and speculative interest. This volatility can present both opportunities and risks for investors, influencing their investment decisions. The stability of CBDCs may attract more conservative investors, while the high-risk, high-reward nature of cryptocurrencies continues to appeal to those seeking substantial returns.
Potential Impacts of CBDCs on Crypto Investments

The emergence of CBDCs is set to reshape the landscape of crypto investments significantly. CBDCs could streamline global payments and foster a more efficient financial system by enhancing cross-border transactions and eliminating the complexities associated with traditional financial intermediaries. The digital yuan (e-CNY), for instance, has already reached impressive transaction volumes, highlighting the potential scale and impact of these digital currencies.
As CBDCs become more prevalent, their influence on market dynamics and investment strategies will become increasingly apparent. Research predicts that global payments using CBDCs will grow significantly in the coming years, further integrating these digital currencies into the financial ecosystem.
The coexistence of different types of CBDCs within the same economy suggests a harmonious relationship with cryptocurrencies, rather than outright competition.
Market Dynamics
CBDCs could offer a stable alternative to cryptocurrencies, encouraging a coexistence that stabilizes the market rather than disrupts it. The value of cryptocurrencies is largely dictated by investor sentiments and market dynamics, which can result in significant price volatility. The introduction of a stable digital currency like a CBDC could attract more traditional investors, providing a balance to the speculative nature of the crypto market.
This potential for stability might also drive innovation within the cryptocurrency space, as developers and investors seek to differentiate their offerings in an increasingly competitive environment. By providing a secure and regulated digital currency, CBDCs could enhance the overall legitimacy of digital finance, encouraging broader adoption and investment.
Investment Strategies
The rapid implementation of CBDCs requires careful planning to avoid systemic economic instability. The impact of CBDCs on financial systems may prompt crypto investors to reassess their investment strategies. Staying informed about CBDC developments and their potential market impacts is crucial for adjusting investment strategies accordingly.
Investors should consider the broader financial landscape, including interest rates, monetary policies, and regulatory efforts, as they explore new investment opportunities. Understanding the potential risks and rewards associated with CBDCs enables investors to make more informed decisions and develop strategies that leverage the strengths of both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies.
Opportunities for Crypto Investors
The introduction of CBDCs presents several opportunities for crypto investors. By enhancing the legitimacy of digital currencies, CBDCs could attract more traditional investors, increasing market participation and liquidity. Additionally, CBDCs have the potential to lower transaction costs in cryptocurrency payments, making them more appealing to users.
These new avenues for investment, particularly in technologies that support CBDC infrastructure, offer exciting prospects for growth and innovation. As the financial landscape evolves, crypto investors can capitalize on these opportunities to diversify their portfolios and explore emerging markets.
Enhanced Financial Inclusion
CBDCs can significantly improve access to financial services for the unbanked population, providing new investment opportunities and enhancing financial inclusion. CBDCs can facilitate digital payments and overall financial management by offering individuals without bank accounts access to essential financial services.
CBDCs can increase accessibility for those traditionally excluded from financial systems, opening up new investment opportunities in decentralized finance (DeFi) and smart contract applications. For instance, the Eastern Caribbean Central Bank’s DCash initiative aims to enhance payment efficiency across its member countries, illustrating the potential for regional impact.
Integration with Blockchain Technology
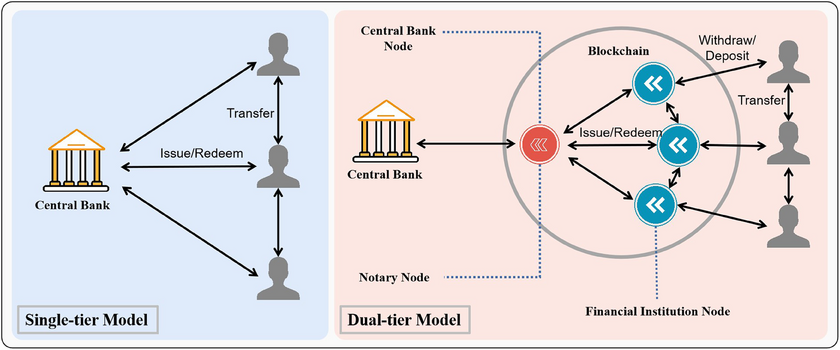
CBDCs can leverage existing distributed ledger technology to improve transaction efficiency and security within the financial system. Utilizing blockchain for CBDCs can eliminate intermediaries, enabling real-time transaction validation and enhancing overall security.
Countries exploring CBDCs are integrating them with decentralized finance solutions, suggesting a trend toward hybrid financial systems that combine government oversight with DeFi’s innovation. This interoperability between CBDCs and DeFi frameworks is expected to define the evolution of digital currencies, reshaping how people exchange value globally.
Risks Associated with CBDCs for Crypto Investors
While CBDCs offer numerous opportunities, they also come with risks that crypto investors must consider. Increased security features of CBDCs compared to traditional cryptocurrencies may shift investor confidence towards CBDCs. Additionally, the volatility and lack of regulation associated with cryptocurrencies present significant financial risks.
Governments face challenges with cryptocurrencies due to concerns over criminal activities, environmental impacts, and consumer protection. These issues could influence the regulatory landscape and potentially affect the attractiveness of cryptocurrencies relative to CBDCs.
Regulatory Risks
The lack of international regulatory frameworks for CBDCs can lead to legal ambiguities and potential jurisdictional conflicts. Compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CFT) regulations is essential to mitigate illicit activities. However, efforts to adopt CBDCs, such as the DCash in the Eastern Caribbean, have faced challenges in the process, including low engagement from both consumers and merchants.
Privacy concerns are another significant risk, as CBDCs could enable the tracking of individuals’ financial transactions, raising concerns about increased surveillance that may deter some users and investors, impacting the overall adoption and success of CBDCs.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The digital nature of CBDCs raises significant cybersecurity risks, necessitating robust security measures to protect users. Dependence on technology for financial transactions introduces risks related to system failures and cyber-attacks, which could undermine confidence in digital currencies.
Governments and financial institutions must address privacy and security concerns when implementing CBDCs to ensure widespread adoption and maintain trust in the financial system. Balancing innovation with consumer protection will be crucial in navigating the risks associated with CBDCs, as they must provide the same protections to users.
Case Studies: Countries Implementing CBDCs
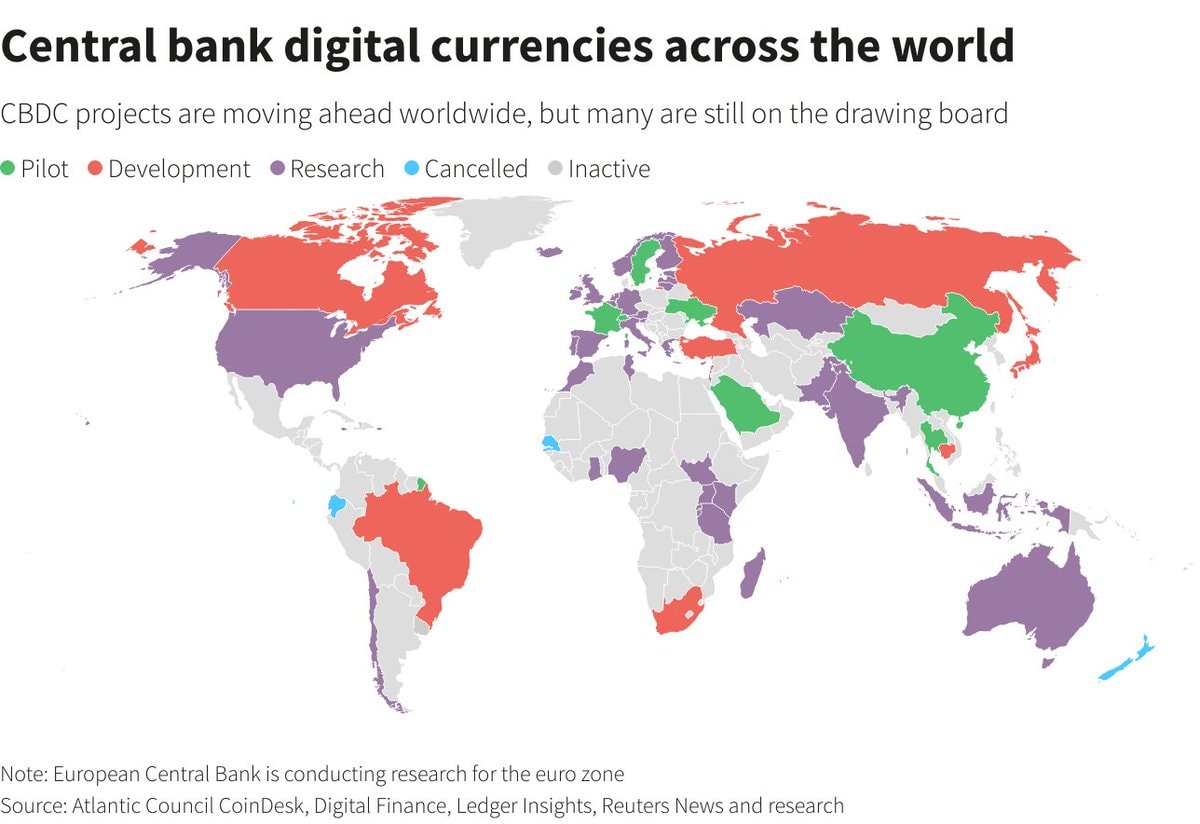
Several countries have already implemented CBDCs, providing valuable insights into their potential impact on the financial landscape. The Bahamas, Jamaica, and Nigeria are examples of a country that has fully launched CBDCs, each with unique approaches and objectives, showcasing the country’s commitment to innovation.
These case studies illustrate the diverse ways in which CBDCs can promote financial inclusion and innovation, offering lessons for other nations considering their own digital currencies. The experiences of these countries highlight both the opportunities and challenges associated with CBDC implementation.
China’s Digital Yuan
China’s digital yuan (e-CNY) is a pioneering example of a central bank digital currency aimed at modernizing the domestic payments system. Designed to replace physical cash, the digital yuan facilitates everyday transactions while being monitored by the People’s Bank of China.
This initiative has the potential to influence the global cryptocurrency landscape, introducing competition and regulatory challenges. As the world’s largest CBDC pilot project, the digital yuan offers valuable insights into the future of digital currencies and their integration into the global economy.
Eastern Caribbean Currency Union
The Eastern Caribbean Currency Union has introduced a CBDC as part of its efforts to modernize the region’s monetary system. Several pilot programs are underway to test the functionality and acceptance of the CBDC among member states.
The introduction of the CBDC is expected to significantly influence the regional crypto markets, creating a more regulated environment and possibly easing access to digital currencies. Investors in the Eastern Caribbean may witness a shift in dynamics as CBDCs coexist with existing crypto assets, leading to new investment opportunities and challenges.
Future Outlook for CBDCs and Cryptocurrencies
The future landscape of finance will likely see increased integration of CBDCs and cryptocurrencies, with regulatory frameworks evolving to accommodate both. This evolution may lead to a hybrid financial system that capitalizes on the strengths of both digital currencies.
The Digital Yuan initiative by China is a major move to establish a more controlled digital economy and potentially lessen reliance on the U.S. digital dollar. The adoption of CBDCs by more countries will shape the future of finance, influencing investment strategies and market dynamics through their interplay with cryptocurrencies.
Coexistence and Competition
The introduction of CBDCs may fundamentally change the cryptocurrency market, affecting investor confidence and market valuation. The coexistence of CBDCs and cryptocurrencies could create a hybrid financial ecosystem where both forms of digital currency serve distinct roles. This dynamic requires crypto investors to remain vigilant, as CBDCs could pose regulatory challenges and impact cryptocurrency pricing.
Market dynamics may shift, with the stability provided by CBDCs attracting traditional investors away from the more volatile cryptocurrencies. However, this increased competition could also drive innovation within the cryptocurrency space, offering new opportunities for investors who are willing to adapt to the evolving landscape.
While CBDCs could stabilize the market, they also introduce risks such as regulatory scrutiny and competitive pressures on cryptocurrencies.
Long-term Predictions
Long-term predictions suggest that the interaction between CBDCs and cryptocurrencies will significantly redefine financial transactions and investment strategies. Experts anticipate that while CBDCs will gain traction, cryptocurrencies will remain relevant due to their decentralized nature and the growing demand for alternative financial solutions.
This evolving dynamic is expected to create a financial ecosystem where both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies coexist, influencing investor strategies and market sustainability. New financial frameworks will likely emerge, enhancing efficiency and creating innovative investment opportunities.
Investors must stay informed and adaptable as the landscape evolves to capitalize on the potential benefits of both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies.
Summary
In summary, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) represent a significant shift in the financial landscape, offering a stable and regulated alternative to traditional cryptocurrencies. While CBDCs and cryptocurrencies have fundamental differences, they also present unique opportunities and challenges for investors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the evolving world of digital finance.
As CBDCs continue to gain traction, they will influence market dynamics, investment strategies, and financial inclusion. The coexistence of CBDCs and cryptocurrencies will likely shape the future of finance, creating a hybrid ecosystem that leverages the strengths of both digital currencies. By staying informed and adaptable, investors can capitalize on the opportunities presented by this new era of digital finance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)?
CBDCs are digital versions of a country’s fiat currency issued by central banks, aimed at providing a secure and regulated digital asset for public use. This innovation enhances monetary policy and financial inclusion while offering a stable alternative to cryptocurrencies.
How do CBDCs differ from cryptocurrencies?
CBDCs are backed and regulated by central authorities to ensure stability, whereas cryptocurrencies function in a decentralized environment and often exhibit significant price volatility.
What are the potential impacts of CBDCs on crypto investments?
CBDCs may significantly impact crypto investments by providing a stable alternative that could alter market dynamics and encourage investors to reevaluate their strategies. This shift could lead to increased competition and changes in investment behavior within the cryptocurrency space.
What opportunities do CBDCs present for crypto investors?
CBDCs enhance the legitimacy of cryptocurrencies and can lower transaction costs, presenting new investment opportunities in related technologies. This evolution may open new avenues for crypto investors to explore.
What are the privacy and security concerns associated with CBDCs?
The implementation of CBDCs poses notable cybersecurity risks and privacy issues, underscoring the need for strong security measures to safeguard user information.

