Comparing Crypto Blockchains: Best Platforms of 2024
Comparing crypto blockchains helps you find the best platform for your needs. This article explores the key features of leading blockchain platforms in 2024, offering insights into their strengths and differences.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain technology is essential for secure, decentralized applications, with modern platforms focusing on scalability, performance, and energy efficiency.
- Different types of blockchain networks—public, private, consortium, and hybrid—offer unique features and advantages tailored to specific use cases.
- Leading blockchain platforms in 2024, such as Ethereum, Solana, and Polkadot, are recognized for their advanced capabilities, consensus mechanisms, and robust developer ecosystems.
Comparing Crypto Blockchains: Best Platforms of 2024
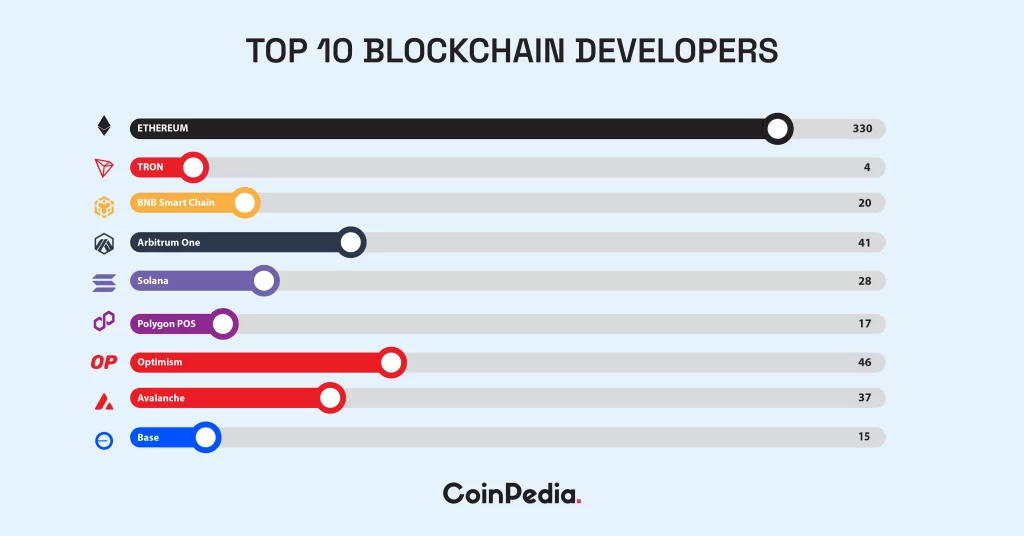
Blockchain technology is crucial for cryptocurrencies, providing a secure, decentralized ledger. It has unlocked numerous opportunities across industries, enabling innovative blockchain-based applications. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain fosters a trust system based on consensus mechanisms to verify and include transactions in blocks, ensuring a single version of the truth across a distributed network of nodes.
Modern blockchain platforms aim to address the limitations of earlier systems, such as high energy consumption and slow transaction speeds. Scalability is a major focus, with platforms developing solutions to handle higher transaction volumes efficiently. Immutability is another key feature, ensuring that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, thereby enhancing data integrity.
Selecting the appropriate blockchain framework is vital for creating decentralized applications tailored to specific needs.
Introduction
Comparing blockchain platforms helps users make informed decisions in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Understanding blockchain technology is crucial for engaging with the crypto space. Novices can benefit greatly from detailed guidance on selecting the right blockchain platform.
Navigating blockchain technology can be daunting. This guide serves as a navigational tool, offering insights to compare leading blockchain platforms of 2024. Understanding each platform’s nuances and benefits will help you make decisions aligned with your goals.
Understanding Blockchain Protocols
Blockchain technology underpins cryptocurrencies with a secure, decentralized ledger. Modern platforms aim to overcome past limitations, such as energy consumption and speed, opening opportunities for blockchain applications across industries and eliminating intermediaries to build direct trust among users.
A blockchain protocol acts as the foundational code layer for blockchain activity, ensuring accurate transaction handling. Key characteristics of blockchain technology include immutability, where recorded transaction data cannot be altered, thereby enhancing security.
Consensus mechanisms are crucial for verifying transactions into blocks, supporting the network’s integrity. Scalability is another critical aspect, referring to the network’s capacity to handle higher transaction volumes while maintaining performance.
Types of Blockchain Networks
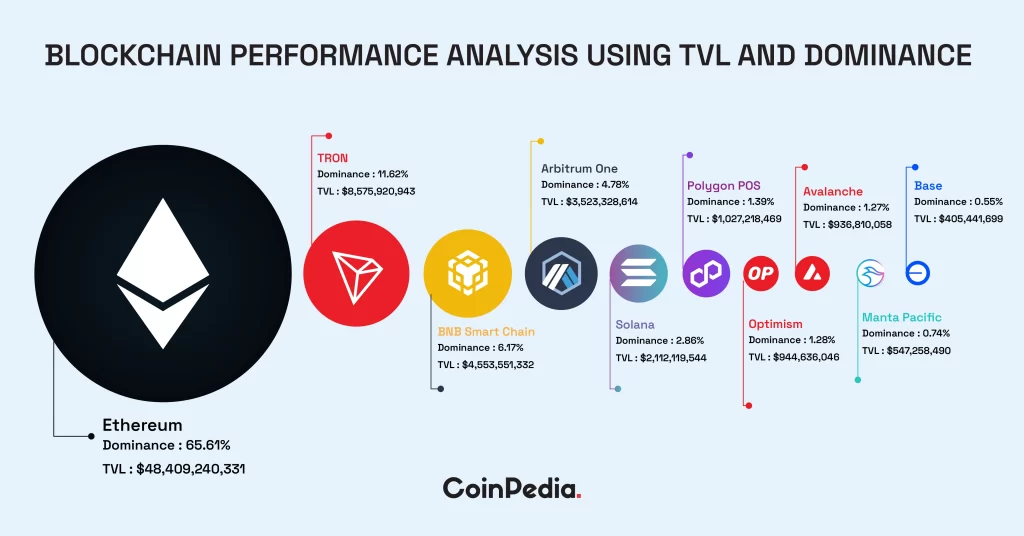
Blockchain networks can be categorized into four major types: public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchain network. Public blockchains prioritize decentralization, promoting an inclusive system resistant to control by single entities. They are open to anyone, allowing unrestricted access and participation in transactions. This openness makes them ideal for applications that require transparency and trust, such as cryptocurrencies.
Private blockchains, on the other hand, operate in a closed environment with access limited to authorized participants, typically within an organization. They can be customized to meet specific organizational needs, providing flexibility for various business scenarios.
Consortium blockchains combine features of public and private networks, facilitating collaboration while maintaining some level of decentralization. They are managed by multiple organizations, allowing shared control and decision-making among participants. A notable advantage is cost-sharing among member organizations, reducing individual financial burdens.
Recognizing the unique features and potential applications of different blockchain platforms is crucial. Public blockchains offer transparency, while private ones provide secure, controlled access. Each type has distinct advantages and caters to specific use cases.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
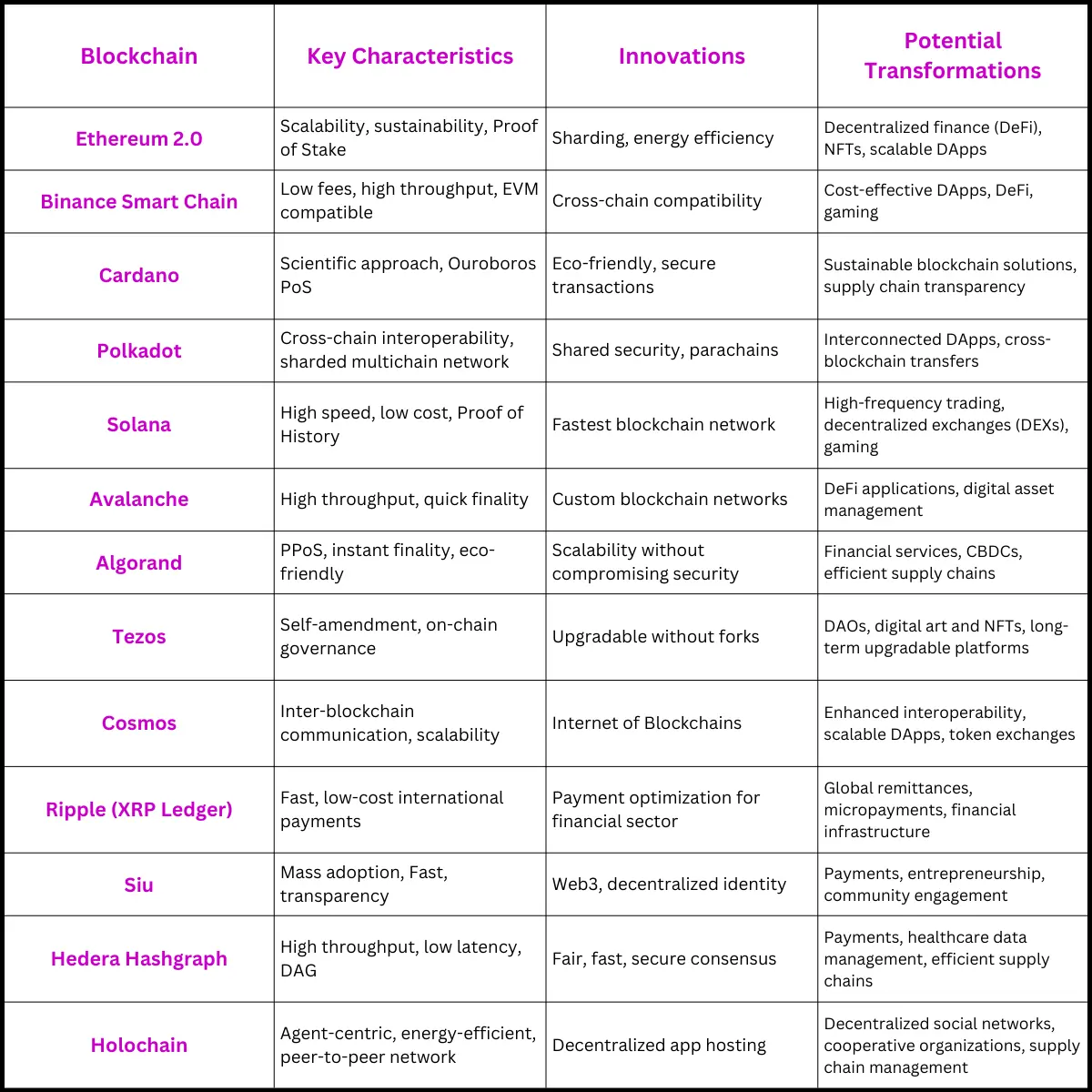
Immutability, a critical feature of blockchain technology, ensures data recorded cannot be changed or deleted, providing a permanent, tamper-proof record. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring high trust and data integrity, like financial transactions and supply chain management.
Another hallmark of blockchain technology is transparency. A secure, publicly accessible ledger enhances transparency, enabling efficient asset and transaction tracking. Consensus mechanisms maintain data accuracy and integrity, ensuring all participants agree on transaction validity.
Decentralization distributes control across various nodes instead of a central authority, enhancing security and resilience. Decentralized finance (DeFi) exemplifies these features, creating robust financial systems without intermediaries. Leveraging blockchain’s immutability, transparency, consensus, and decentralization, DeFi platforms offer innovative, accessible, and secure financial services.
Major Blockchain Platforms in 2024
In 2024, several blockchain platforms are notable for their innovative features and robust performance. Here are the top frameworks:
- R3 Corda, which offers unique capabilities tailored to specific business needs
- Hyperledger, known for its modular architecture and enterprise-grade solutions
- Ethereum, recognized for its smart contract functionality and decentralized applications
Each of these platforms provides distinct advantages depending on the use case.
Klaytn, an open-source service-oriented blockchain by Ground X, features decentralized data, distributed governance, low latency, and high scalability. Tezos supports a self-amending cryptographic mechanism, enabling seamless upgrades and new features.
Fantom allows the creation and deployment of independent networks to enhance scalability and reduce congestion. Key parameters for evaluating blockchain platforms in 2024 include scalability, security, transaction fees, and governance.
Ethereum

Proposed by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 and launched on July 30, 2015, Ethereum remains a leading blockchain platform. Its developer ecosystem includes tools like Truffle, Remix IDE, and Scaffold-ETH, essential for writing decentralized applications. Ethereum’s versatility and broad adoption make it a favored platform for developers and enterprises.
The platform’s support for smart contracts has revolutionized the way applications are built and deployed, enabling a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) across various sectors. Its compatibility with other blockchain platforms, such as Hyperledger Fabric, further enhances its utility and integration capabilities.
Binance Smart Chain
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) primarily runs smart contract-based dApps, DeFi yield farming, and staking projects. Its native token, Binance Coin (BNB), is crucial to the ecosystem. BSC’s compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) allows developers to port applications from Ethereum to BSC with minimal modifications.
BSC’s speed and low transaction fees make it attractive to developers and users. Its growing ecosystem supports a broad range of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), cementing its status as a major blockchain platform in 2024.
Solana
Solana’s architecture emphasizes high throughput, achieving over 1,000 transactions per second under optimal conditions. Designed for efficiency, scalability, and performance, Solana aims for low latency in transaction processing to ensure a faster user experience.
Solana uses a unique Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus mechanism to timestamp transactions, enhancing efficiency and security. This innovation allows Solana to process transactions at a speed and cost few other blockchains can match, making it a leading choice for high-performance applications.
Cardano
Cardano’s two-layer architecture separates transaction settlement and smart contract execution to enhance scalability. The Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) and Cardano Computational Layer (CCL) allow for efficient processing and flexibility. Cardano’s Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism promotes network sustainability.
Cardano’s native currency, Ada, is crucial for transactions and governance within its ecosystem. Co-founded by Charles Hoskinson, Cardano continues to innovate and lead in the blockchain space.
Tron
TRON has become the second-largest public chain for decentralized applications, surpassing EOS. Governance is managed by elected Super Representatives through decentralized voting. In December 2021, TRON transitioned to a fully decentralized, community-governed organization known as a DAO.
TRON employs a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) mechanism for consensus. The ecosystem relies on twenty-seven super representatives (SRs) to validate transactions. Smart contracts on the TRON network are developed using Solidity and other advanced programming languages.
Sui
Sui combines Web3 technology advantages with the user-friendly experience of Web2. It offers secure on-chain storage for assets, adapting to user requirements. Sui uses a unique consensus and transaction processing method, enhancing efficiency compared to conventional blockchains.
Sui Blockchain, developed by Mysten Labs and specifically catering to the Web3 and NFT sectors, comprises former Meta’s Novi Research executives. Its native token, SUI, has a total supply of ten billion tokens.
Sui’s smart contracts use the Move programming language, emphasizing security while minimizing coding requirements.
Polkadot
Polkadot enables different blockchains to transfer messages and value trust-free, addressing scalability and interoperability issues. Its multi-chain framework allows multiple chains (parachains) to operate in parallel, improving network scalability and efficiency. Parachains run in parallel on Polkadot, allowing them to send messages and share security.
Polkadot’s cross-chain interoperability features enable seamless interaction between various blockchain ecosystems, fostering a connected blockchain landscape. Solutions like Wormhole and Axelar Network enhance interoperability by enabling value and information transfer between Polkadot and other blockchain networks.
Comparing Scalability and Performance

Scalability and performance are critical metrics when evaluating blockchain platforms. Time to finality, or how long it takes for a transaction to be permanently recorded, is a key consideration. Ethereum’s practical transaction throughput is around 14 TPS, less than its theoretical maximum of 119 TPS. The Ethereum community has shifted from sharding to Proto-Danksharding to enhance transaction capacity.
Cardano’s theoretical transaction capacity is approximately 386 TPS, with an average of about 2 TPS currently processed. Solana can theoretically handle around 65,000 TPS under optimal conditions. Avalanche’s C-Chain processes about 3.5 TPS, while the entire network, including subnets, handles approximately 15.5 TPS.
Algorand can theoretically achieve up to 6,000 TPS, aiming for 10,000 TPS through future upgrades. The Internet Computer platform processes around 6,000 TPS in practice, benefiting from quick finality times.
Public blockchains may struggle with scalability during high transaction volumes, impacting processing times and high gas fees. Gas fees rise with increased demand due to the demand-supply dynamic.
Security and Consensus Mechanisms
Security and consensus mechanisms are fundamental to the reliability and trustworthiness of blockchain platforms. Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake validate transactions, ensuring all participants agree on the blockchain’s state. These mechanisms are crucial for maintaining reliability and security within blockchain networks, enhancing the blockchain’s integrity by achieving a uniform state across all nodes.
Blockchain uses cryptographic methods to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized alterations, making it resistant to censorship and fraud. Its decentralized design functions as a distributed ledger, ensuring data integrity and security. A robust consensus mechanism reduces vulnerability to fraud and attacks. For instance, Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake significantly reduced its energy consumption by approximately 99.95%.
Different platforms use various consensus algorithms tailored to their needs. Here are a few examples:
- Hyperledger Sawtooth supports Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance and incorporates Proof of Elapsed Time for enterprise solutions.
- Hedera Hashgraph employs an Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus algorithm, enhancing resilience against attacks.
- EOS utilizes a Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance algorithm to enhance transaction processing speed and efficiency.
Enterprise Solutions and Use Cases
The growth of blockchain platforms has significantly accelerated due to their applications in streamlining supply chains and enhancing traceability. Blockchain technology enhances privacy in transactions while maintaining transparency through cryptographic addresses. These features make blockchain platforms increasingly attractive for enterprise solutions, particularly in sectors where multiparty cooperation or data sharing is essential.
The transparent nature of blockchain instills confidence among stakeholders, as all transactions can be verified in real-time without the risk of manipulation. This transparency, coupled with the ability to address scalability issues, positions blockchain as a transformative technology for enterprises looking to innovate and improve operational efficiency.
Ecosystem and Developer Support
The ecosystem and developer support provided by blockchain platforms are crucial for their adoption and success. Cosmos enables the creation of application-specific blockchains through the Ignite CLI, simplifying development and management. Polkadot uses a framework called Substrate for building blockchains, allowing developers to create custom logic through modular components known as pallets.
Solana’s development utilizes tools like Dapp-Scaffold and Anchor, focusing on building smart contracts mostly in Rust. Tezos supports a dynamically upgradeable protocol that allows developers to add new features seamlessly.
Robust development tools and frameworks are essential for effective blockchain development, enabling developers to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently.
Governance Models
Governance models in blockchain platforms play a vital role in their operation and evolution. On-chain governance allows decisions to be made through direct voting on the blockchain, promoting decentralization. Off-chain governance involves decision-making by a designated group outside the blockchain, which can enhance efficiency but may lead to centralization. Hybrid governance models merge both on-chain and off-chain elements to balance decentralization and efficiency.
Achieving consensus on protocol changes is a significant challenge in blockchain governance, which can lead to network forks if unresolved. The effectiveness of a governance model is influenced by the project’s objectives, community dynamics, and desired level of decentralization.
To enhance transparency and trust, formal governance structures such as Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) can be established.
Transaction Fees and Cost Efficiency
Transaction fees and cost efficiency are critical considerations for users and developers on blockchain platforms. Bitcoin’s average transaction fee has increased over 200% in the past year, currently reaching approximately $6.96. Higher transaction fees often correlate with faster processing times during periods of high network activity. Different blockchains have distinct fee structures influenced by factors like transaction size and network conditions.
Ethereum’s transaction fees can vary significantly based on the complexity of smart contracts involved. Complications in transactions, like those involving multiple state changes, can increase associated fees. Users can potentially reduce fees by transacting during off-peak hours or utilizing Layer-2 solutions.
As blockchain technology evolves, fee trends may change due to new scaling solutions and regulatory influences.
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions
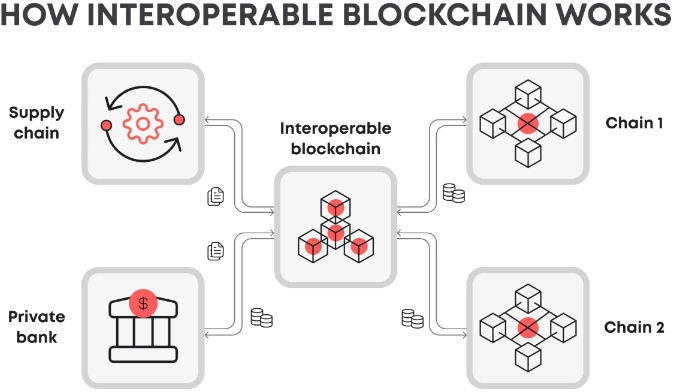
Interoperability in blockchain allows different networks to work together seamlessly, improving data sharing and collaboration across organizational boundaries. Polkadot’s multi-chain framework allows different blockchains, or parachains, to interoperate seamlessly, promoting cross-chain functionalities. Blockchain Links, termed ‘Blinks’, are designed to connect various blockchain systems, enhancing interoperability and allowing seamless data and asset transfers.
Blinks facilitate cross-chain communication, enabling different blockchains to exchange information and overcome traditional isolation. Solutions like Solana Blinks focus on high-performance interoperability, allowing efficient token transfers and data sharing between networks. Cronos Blinks emphasize compatibility with Ethereum’s EVM, making it easier for Ethereum-based applications to interact with the Cronos network.
Interoperability and cross-chain solutions are crucial for the growth and adoption of blockchain technology, particularly in enterprise solutions and decentralized finance. By enabling seamless interaction between various blockchain platforms, these solutions enhance the overall functionality and utility of blockchain networks.
Summary
As we have explored, blockchain technology offers a myriad of benefits, including decentralization, transparency, and security. Each blockchain platform has its unique strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of platform depends on specific needs and use cases. Ethereum remains a versatile and widely adopted platform, while Binance Smart Chain offers speed and low transaction fees. Solana excels in scalability and performance, and Cardano provides a sustainable and scalable solution with its dual-layer architecture.
In conclusion, understanding the key features, scalability, security mechanisms, and governance models of various blockchain platforms is essential for making informed decisions in this rapidly evolving digital landscape. By leveraging the strengths of each platform, developers, enterprises, and users can unlock the full potential of blockchain technology and drive innovation across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes blockchain technology secure?
Blockchain technology is secure due to its use of cryptographic methods and consensus mechanisms, which ensure transaction integrity and prevent unauthorized changes. This inherent design makes it resistant to censorship and fraud.
How does interoperability benefit blockchain platforms?
Interoperability enhances blockchain platforms by enabling seamless collaboration and data sharing across different networks, ultimately improving their overall functionality and utility. This integration fosters greater efficiency and innovation in the blockchain ecosystem.
Why are transaction fees important in blockchain networks?
Transaction fees are crucial as they incentivize miners and validators to process transactions, thereby enhancing the overall security of the blockchain network. Without these fees, the stability and efficiency of transaction processing could be compromised.
What is the significance of governance models in blockchain?
Governance models are crucial in blockchain as they shape decision-making processes, impacting the network’s decentralization, efficiency, and adaptability. Their structure—whether on-chain, off-chain, or hybrid—directly affects the blockchain’s overall performance and evolution.
How do scalability solutions impact blockchain performance?
Scalability solutions significantly enhance blockchain performance by increasing transaction capacity, reducing latency, and lowering fees. This ultimately leads to a more efficient and user-friendly blockchain ecosystem.

